java泛型的概念
实际上java中泛型的实现只是一个语法糖,在编译的时候会起作用,帮我们做一些校验,比如String类型的List是否添加了Integer类型的对象。而该校验在编译后会被“擦除”,所以你可以在运行期间跳过泛型检测(例如反射),我们可以实验证实一下。
先写个简单使用泛型的例子:
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TestGeneric {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("hello");
}
}
然后编译一下,将编译后的class反编译后发现并没有表示集合的类型:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class TestGeneric
{
public static void main(String[] paramArrayOfString)
{
ArrayList localArrayList = new ArrayList();
localArrayList.add("hello");
}
}
通过反射来将一个int类型值添加到List
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by jianlin on 04/19/2018.
*/
public class TT {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("hello");
try {
Method method = List.class.getMethod("add", Object.class);
method.invoke(list, 1);
System.out.println(list);//[hello, 1]
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
既然运行期间都不起作用了,我们还能动态获取到泛型的类型吗?
答案是可以的。 在JDK1.5后对class信息也作了相应调整,将泛型的信息加入了class信息中,且可以通过反射来获取这些信息。
动态获取泛型Class类型
代码实现
- 先编写一个抽象父类,里面定义了一个逻辑就是将泛型T的类型赋值给成员变量type,然后子类可以通过getType()方法来获取type值。
import static com.google.common.base.Preconditions.checkArgument;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
/**
* Created by jianlin on 04/18/2018.
*/
public abstract class AbstractType<T> {
private final Class<T> type;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected AbstractType() {
Type superclass = getClass().getGenericSuperclass();
checkArgument(superclass instanceof ParameterizedType,
"%s isn't parameterized", superclass);
Type runtimeType = ((ParameterizedType) superclass).getActualTypeArguments()[0];
type = (Class<T>) TypeToken.of(runtimeType).getRawType();
}
protected Class<T> getType() {
return type;
}
- 编写几个子类实现,指定T为不同的类型,看看是否能打印出对应的类名。
public class IntegerType extends AbstractType<Integer> {
IntegerType() {
super();
}
}
public class StringType extends AbstractType<String> {
StringType() {
super();
}
}
public class ListType extends AbstractType<List<Integer>> {
ListType() {
super();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntegerType integerType = new IntegerType();
System.out.println(integerType.getType());//class java.lang.Integer
StringType stringType = new StringType();
System.out.println(stringType.getType());//class java.lang.String
ListType listType = new ListType();
System.out.println(listType.getType());//interface java.util.List
}
}
可以看到结果是OK的,所以我要在AbstractType类里实现反序列化的需求可以实现。
原理分析
####
前面提到了class类信息里有包含泛型类信息,用javap -p -v StringType反编译.class文件可以证实这点:
Classfile /Users/jianlin/dev/workspaces/selfworkspaces/codingTest/target/classes/blog/StringType.class
Last modified 2018-4-21; size 332 bytes
MD5 checksum 31016206efd492583f5e1d7fd2646d7c
Compiled from "StringType.java"
public class blog.StringType extends blog.AbstractType<java.lang.String>
minor version: 0
major version: 52
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SUPER
Constant pool:
#1 = Methodref #3.#15 // blog/AbstractType."<init>":()V
#2 = Class #16 // blog/StringType
#3 = Class #17 // blog/AbstractType
#4 = Utf8 <init>
#5 = Utf8 ()V
#6 = Utf8 Code
#7 = Utf8 LineNumberTable
#8 = Utf8 LocalVariableTable
#9 = Utf8 this
#10 = Utf8 Lblog/StringType;
#11 = Utf8 Signature
#12 = Utf8 Lblog/AbstractType<Ljava/lang/String;>;
#13 = Utf8 SourceFile
#14 = Utf8 StringType.java
#15 = NameAndType #4:#5 // "<init>":()V
#16 = Utf8 blog/StringType
#17 = Utf8 blog/AbstractType
{
blog.StringType();
descriptor: ()V
flags:
Code:
stack=1, locals=1, args_size=1
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method blog/AbstractType."<init>":()V
4: return
LineNumberTable:
line 9: 0
line 10: 4
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 5 0 this Lblog/StringType;
}
Signature: #12 // Lblog/AbstractType<Ljava/lang/String;>;
SourceFile: "StringType.java"
然后我们可以通过反射获取对应的类型信息,下面看看获取的方法。
核心代码Type superclass = getClass().getGenericSuperclass();
getClass()方法我们不陌生,就是获取当前类,在前面的例子中就是对应的IntegerType.class等。这里主要看getGenericSuperclass()方法。
/**
* Returns the {@code Type} representing the direct superclass of
* the entity (class, interface, primitive type or void) represented by
* this {@code Class}.
*
* <p>If the superclass is a parameterized type, the {@code Type}
* object returned must accurately reflect the actual type
* parameters used in the source code. The parameterized type
* representing the superclass is created if it had not been
* created before. See the declaration of {@link
* java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType ParameterizedType} for the
* semantics of the creation process for parameterized types. If
* this {@code Class} represents either the {@code Object}
* class, an interface, a primitive type, or void, then null is
* returned. If this object represents an array class then the
* {@code Class} object representing the {@code Object} class is
* returned.
*
* @throws java.lang.reflect.GenericSignatureFormatError if the generic
* class signature does not conform to the format specified in
* <cite>The Java™ Virtual Machine Specification</cite>
* @throws TypeNotPresentException if the generic superclass
* refers to a non-existent type declaration
* @throws java.lang.reflect.MalformedParameterizedTypeException if the
* generic superclass refers to a parameterized type that cannot be
* instantiated for any reason
* @return the superclass of the class represented by this object
* @since 1.5
*/
public Type getGenericSuperclass() {
ClassRepository info = getGenericInfo();
if (info == null) {
return getSuperclass();
}
// Historical irregularity:
// Generic signature marks interfaces with superclass = Object
// but this API returns null for interfaces
if (isInterface()) {
return null;
}
return info.getSuperclass();
}
关于 Type
Type是一个接口,对应的实现类为Class。ParameterizedType是Type的子接口,ParameterizedType的实现类为ParameterizedTypeImpl。
关于 getGenericSuperclass() 方法
该方法返回当前类的直接父类信息(包含泛型参数信息),如果当父类不含泛型信息时,直接返回普通的父类信息。结合前面的例子来解释:
如果类定义是
public class IntegerType extends AbstractType<Integer>,那么返回的Type是ParameterizedTypeImpl对象(包含泛型参数信息,参数见actualTypeArguments)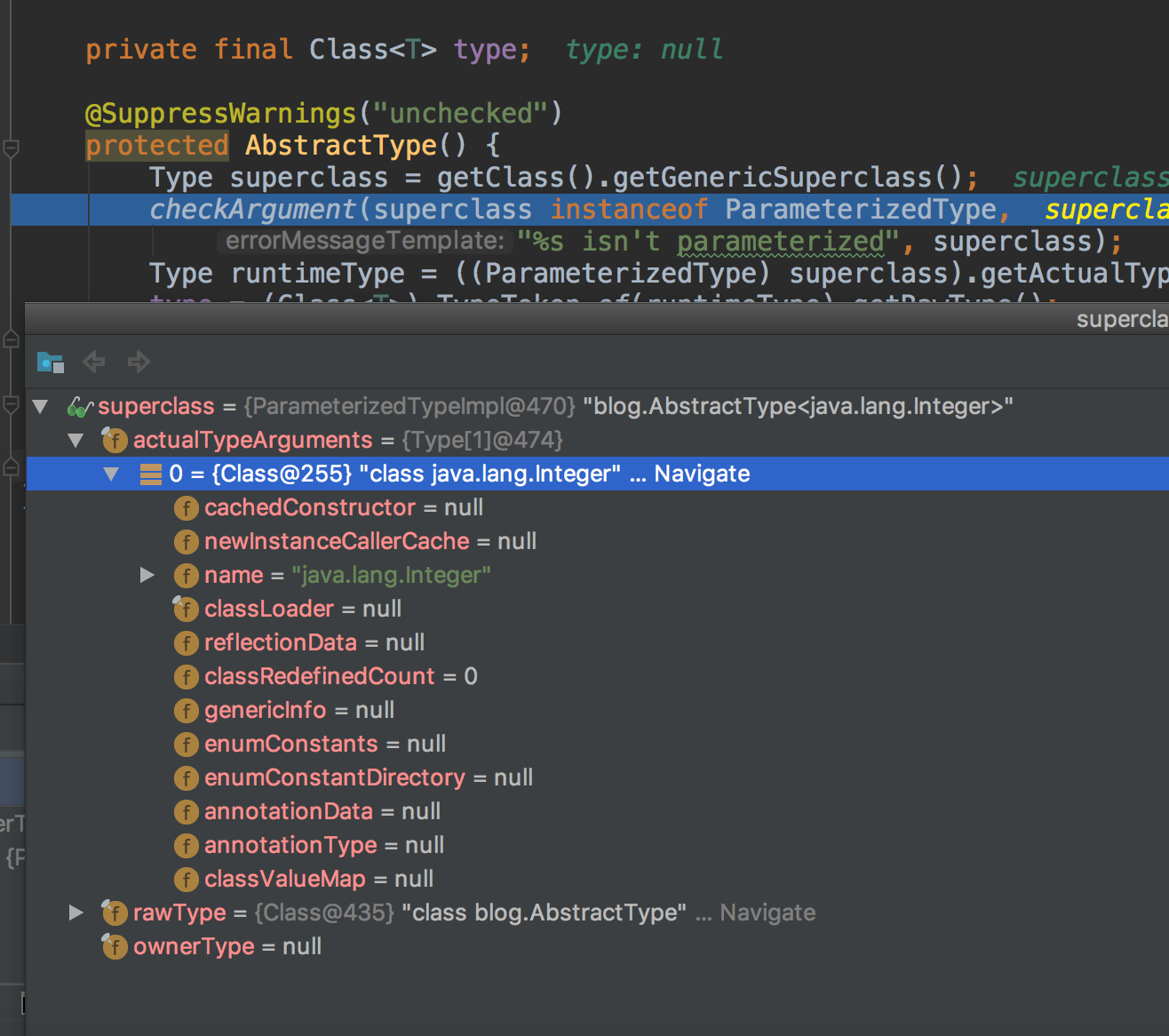
如果类定义为
public class IntegerType extends AbstractType则返回的Type是Class对象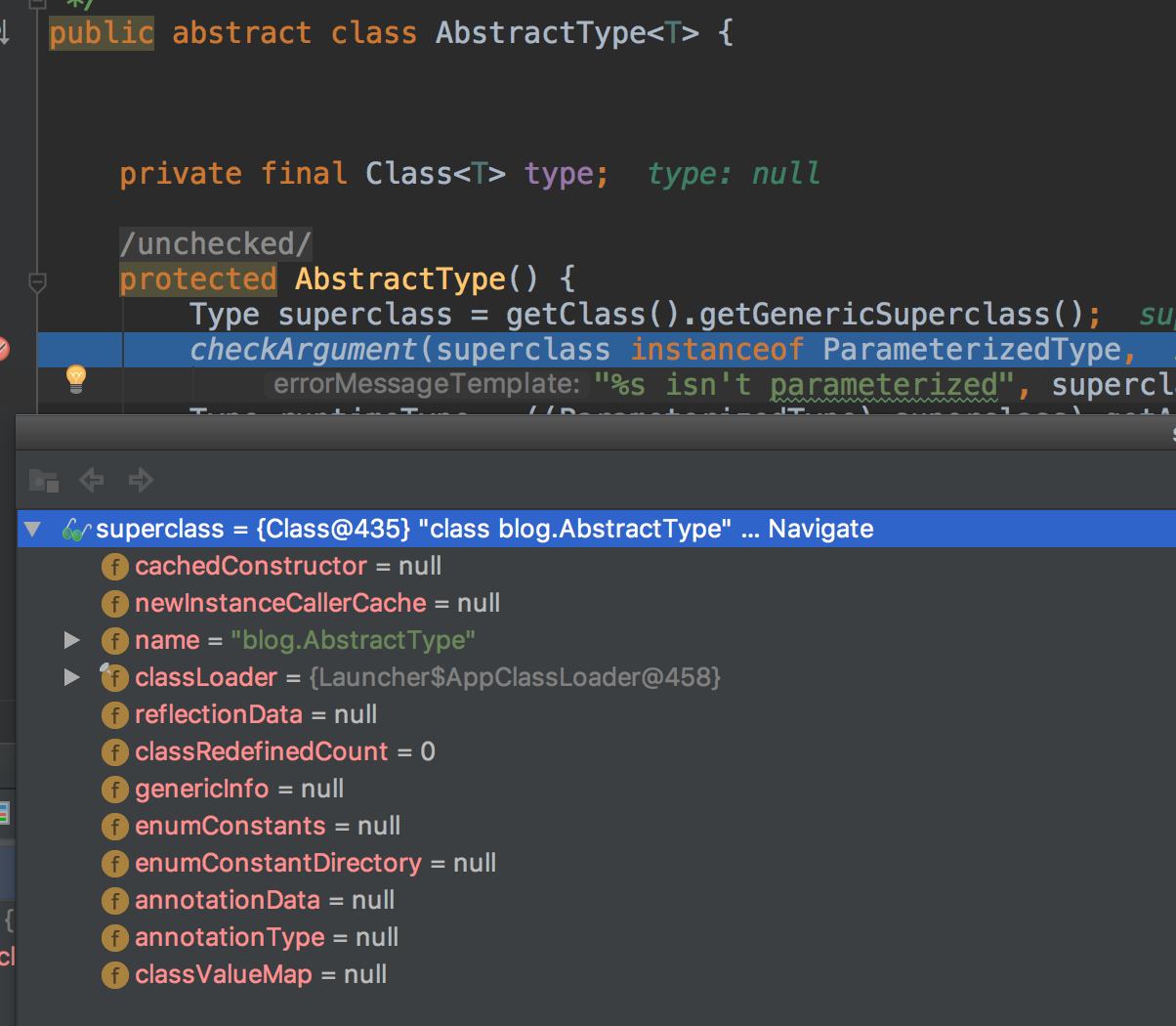
另外如果此类表示Object类,接口,基元类型或void,则返回null。如果此对象表示一个数组类,则返回表示Object类的Class对象
Integer[] array = new Integer[2]; System.out.println(int.class.getGenericSuperclass()); //null System.out.println(Test.class.getGenericSuperclass()); //null Test是定义的接口 System.out.println(Object.class.getGenericSuperclass()); //null System.out.println(void.class.getGenericSuperclass()); //null System.out.println(array.getClass().getGenericSuperclass()); //class java.lang.Object
###获取T类型
最后泛型T到底怎么取呢,细心的同学可能已经发现了,上面的示例图中actualTypeArguments带的数组中第一个类型就是Integer的class对象,那么为啥还要用guava的TypeToken.of处理一下,而不是直接type = (Class
其他方式
实际上Spring也提供了一个动态获取泛型T的Class类型的方法,当然底层还是基于上面提到的getGenericSuperclass()方法实现的,不再做详细描述。
Class<>type = (Class<T>) GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(this.getClass(), AbstractType.class);//spring实现
参考: